# References:
Detection Engineering VS Threat Hunting - Zhihu (zhihu.com)
What is threat hunting - Zhihu (zhihu.com)
A brief discussion on Threat Hunting - FreeBuf Network Security Industry Portal
#threathunting
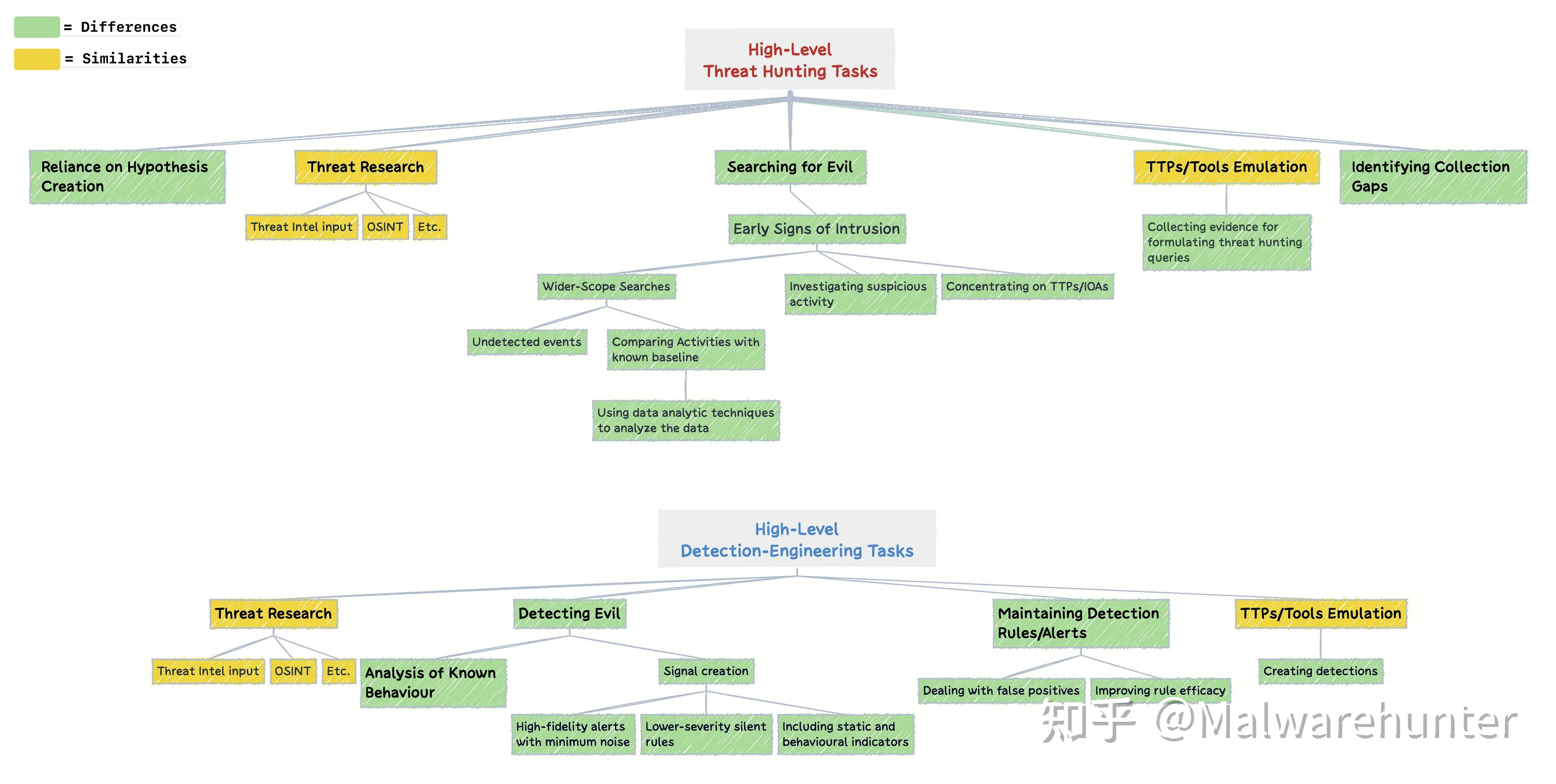
Threat hunting is a proactive security strategy that does not rely on alerts or event notifications from automated tools, but rather on the expertise and intuition of security analysts. The purpose of threat hunting is to proactively search for, identify, and eliminate potential threats in the network that have not yet been discovered by automated systems. This usually involves the following aspects:
- Proactive: Analysts proactively look for unknown, anomalous behaviors or signs in the network.
- Deep Analysis: Use advanced querying, data analysis, and intelligence gathering to explore deeper into your data.
- Expertise Dependence: Rely on the skills and experience of analysts for complex threat identification.
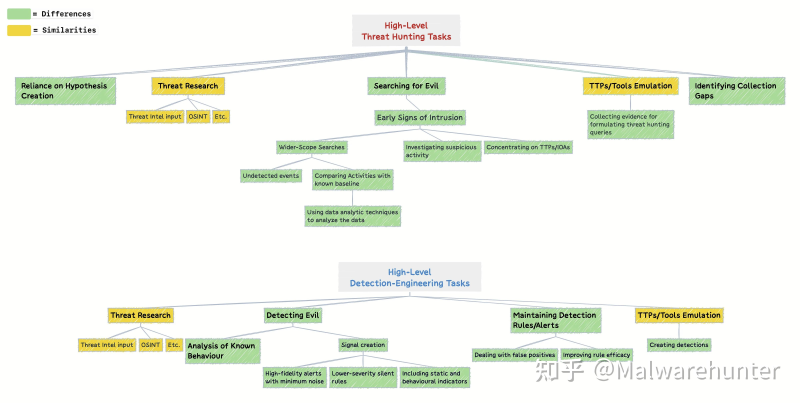
Threat hunting is the practice of proactively searching for evidence of adversarial activity that traditional security systems may miss. It requires actively searching a network or individual host for signs of malicious behavior and anomalies. Detection engineering, on the other hand, is the process of developing and maintaining detection methods to identify malicious activity** after it is known.
In the traceability graph, threat hunting is generally carried out through graph matching\graph alignment. Threat intelligence is often used to construct a query graph, and the query graph and the traceability graph are used for alignment and matching to learn the threat, which is based on the assumption that the threat exists.
The corresponding matching process is shown in the figure below, Gq represents the query graph, and Gp represents the traceability graph. My personal understanding is that DARPA TC data will generate a traceability graph, and then match it with the query graph to produce two corresponding result subgraphs, as shown on the far right. This way we can better discover which part of the subgraph is implementing APT attacks.
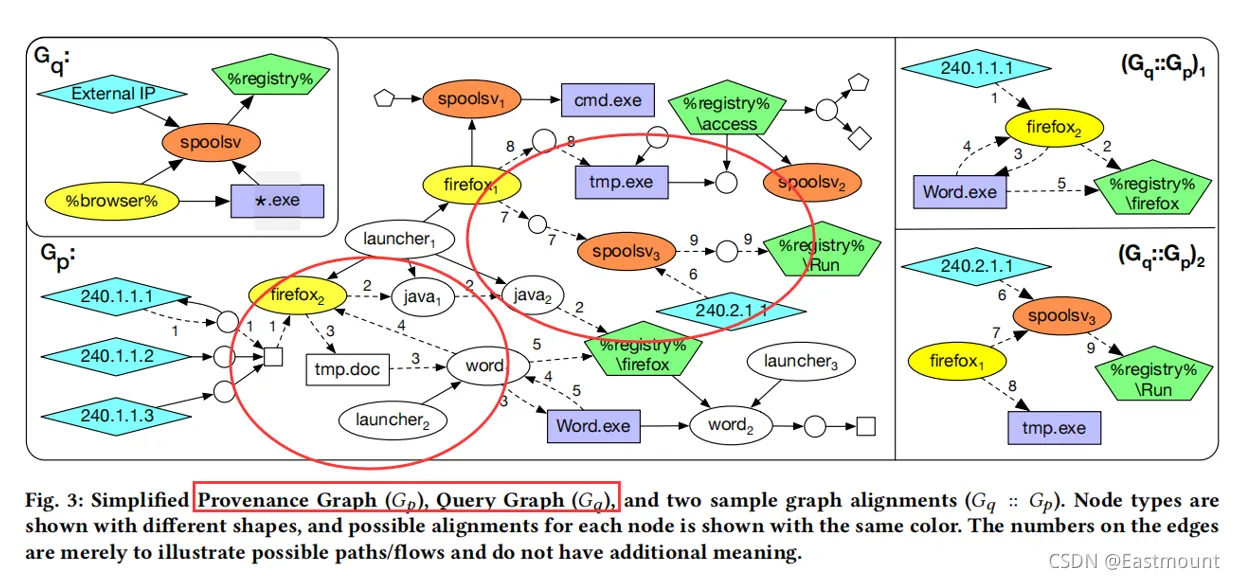
The method also includes two types of alignment: node alignment and graph alignment.
#Threat Detection
Threat detection is the act of identifying and responding to known threats through automated tools. This usually relies on set rules, algorithms and known threat signatures (such as signatures). Threat detection features include:
- Passiveness: Mainly relies on the system’s already defined rules and alerts to identify threats.
- High Automation: Use a variety of automated tools to monitor, analyze, and report suspicious activity.
- Quick Response: Once a known threat is detected, the system can react quickly.
# Similarities and Differences
- Purpose:
- The purpose of threat hunting is to actively look for threats that have penetrated into the network but have not yet been detected, and through in-depth analysis and investigation, discover and remove potential security threats.
- The purpose of threat detection is to monitor network traffic, system logs and other data sources to promptly discover and warn about possible security threat events.
- Method:
- Threat hunting usually involves manual analysis, security intelligence collection, behavioral analysis and other technical means. The focus is on finding and cracking threat behaviors hidden in the system, which usually requires professional security analysts to operate.
- Threat detection relies more on automated tools and technologies, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), security information and event management systems (SIEM), etc. These systems can monitor network traffic and logs in real time to identify possible threatening behaviors.
- Time point:
- Threat hunting is a proactive, periodic activity typically performed by security teams on a regular basis to discover threats that already exist but have not yet been discovered, or to prevent future attacks.
- Threat detection is a continuous, real-time activity that requires continuous monitoring and analysis of network traffic and logs in order to promptly detect and respond to possible security incidents.
- Response:
- For threat hunting, once a potential security threat is discovered, the security team will take appropriate measures to respond to and eliminate the threat, which usually includes patching vulnerabilities, deleting malicious files, blocking attackers, etc.
- For threat detection, once a security incident is detected, the system typically triggers an alert to notify the security team for further investigation and response.
Threat Hunting and Threat Detection are two important concepts in the field of network security. Although they both aim to discover and respond to security threats, their respective focuses and methods are different.
- Same Purpose: Both aim to detect and respond to cybersecurity threats and reduce potential damage.
- Different Approaches: Threat hunting focuses more on a proactive and manual exploration process, while threat detection relies more on automation and existing threat definitions.
- Time Difference: Threat hunting may take longer to identify threats because it relies on in-depth analysis and proactive searches; threat detection responds to known threats faster.